반응형
- each N-bar specifiesa semantic property
- [English teacher]가 하나의 N-bar만 갖고 있다면 --> 의미는 1개 --> (s)he teaches English
- [English teacher]가 두개의 N-bar를 갖고 있다면 --> 의미는 2개 --> (s)the teaches & (s)he is English
- 그렇다면, [a French English teacher]은 어떤 식의 해석이 될까?
- 'a French person who teaches English'일까? 아니면 'an English person who teaches French'일까?
- 답은 항상 'a French person who teaches English'만 된다
- 이유는 word order때문이다
- Complements always come closer to their Heads than Attributes
- English가 teacher에 더 가까워서 Complement
- French가 teacher와 더 멀어 Attribute
- phonological 특징도 있다
- 만약 an ENglish teacher이라면, 이는 'someone who teaches English'이다
- 만약 an ENglish TEAcher이라면, 이는 'a teacher who is English'이다
- 이렇게 stress pattern 차이가 나는 이유는 N-bar에 있다. N-bar는 semantic unit을 나타낸다. 그래서 이 N-bar가 phonological unit을 나타낸다.
- <<결론>> Assign a separate primary stress to each separate N-bar
5. Other Phrases
5.1. Overview
- 우리는 'small' nominal phrase에 대해서 배웠다
- 즉, NP는 N, N-bar, N-double-bar로 나뉘어진다
- 이는 다른 AP, ADVP, PP, VP에도 적용이 된다
- [NP a student of Physics]
- [AP very proud of her son]
- [ADVP quite independently of me]
- [PP right out of the window]
- [VP be thining of her]
- 여기서 각 head인 student, proud, independently, out, thinking 앞에 오는 것은 specifier, 뒤에 오는 것은 complement이다
- 즉, 순서가 Specifier-Head-Complement
- NP의 이러한 구조는 다른 phrase에도 적용 가능하다
- 이를 general하게 표현 가능
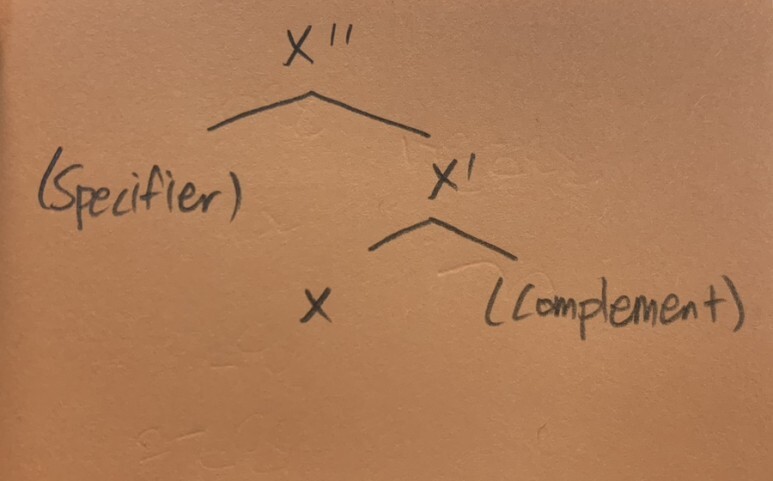
- 모든 종류의 category를 표현하기 위해서 category variable을 활용할 수 있다
- category variable = a symbol which can stand for any category of a given type
- 여기 X위치에는 word-level cateogry를 표현한다
- Speficier와 Complement는 categorial term이 아니다. 얘네들은 grammatical functions or relations을 나타낸다
- 그런데, 이 Specifier와 Complement 모두 optional한 성분이다.
- (예시) [N''students] [A'' proud] [ADV'' independently] [P'' out] [V'' think]
- X는 X'의 head
- X'는 X''의 head
- X는 Ultimate Head
- X'는 (Immediate) Head
- 그래서 Head라고 하면, 2개를 말할 수 있음 = Immediate Head/ Ultimate Head
- 하지만 Head라고 하면, Ultimate Head
5.2. Verb Phrases
- V + Complement = V-bar
- Specifier + V-ber V-double-bar
- V'가 있다는 syntactic 증거 보여주겠다
- 증거 1= V-bar만 fronted가능하다
- (예시) They swore that John might have been taking heroin, and
- ----[V' taking heorin] he might have been
- ----* [VP been taking heroin] he might have!
- ----* [VP have been taking heorin[ he might
- 증거 2= begin 이나 see 다음에 V'를 CPT로 취한다
- (예시) I saw John [V' run down the road]
- (예시) * I saw him [VP be running down the road]
- (예시) * I saw him [VP hhave finished his work]
- Complement와 Adjunct 사이의 차이점은 'internal' postmodifier와 'external' postmodifer에서 비롯
- (예시 1) (a) He will work [at the job] (=internal)
- (예시 1) (b) He will work [at the office] (=external)
- (예시 2) (a) He laughed [at the clown] (=internal)
- (예시 2) (b) He laughed [at ten o'clock] (=external)
- internal로 해석된 것은 Complement이고
- external로 해석된 것은 Adjunct이다
- Complement와 Adjunct의 차이점을 더 살펴보겠다
- 차이점 1= structural ambiguity
- (예시 1) He may decide on the boat
- (예시 2) He couldn't explain last night
- (예시 1) 에서 'on the boat'는 Complement 혹은 Adjunct로 해석 가능하다
- (예시 2) 에서 'last night'도 Complement 혹은 Adjunct로 해석 가능하다
- Comeplement면 within the V-bar contianing the head V
- Adjunct면 outside the V-bar containing the head V
- 차이점 2= passivization
- 수동태는 Complement PP의 NP만 가능하고, Adjunct PP 의 NP는 불가능하다
- (예시) [This job] needs to be worked at by an expert
- (예시) *[This office] is worked at by a lot of people
- 만약에 이미 passivization이 되어있으면, 중의성이 사라진다. 왜냐하면 Complement PP의 NP만 수동태가 가능하니까
- (예시) [The boat] was decided on after lengthy deliberation.
Source: Transformational Grammar by Andrew Radford
반응형
'영어임용원서 > Transformational Grammar' 카테고리의 다른 글
| pp. 244-253 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
|---|---|
| pp. 234-243 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| pp. 204-213 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| pp. 194-203 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| pp. 184-193 (0) | 2023.06.26 |